Tagged Under:
How to Choose the Best AV Receiver
Which one is right for you?
AV receivers act as the central hub in your home system and live up to the acronym in their name by supporting multiple audio and video formats. If you enjoy watching movies and television shows at home, they’re pretty much a necessity, as they do the important job of distributing video to your big-screen TV, monitor and/or projector, along with routing audio to your speaker system.
But there are so many models to choose from! How do you know which one is right for you? Here’s a guide to picking the best AV receiver for your needs.
I/O
The first question you should ask yourself when choosing an AV receiver is, “How many inputs and outputs will I need?” Modern AV receivers typically offer a wide variety of connectors, including one or more HDMI® inputs for connecting video devices such as cable or satellite TV boxes, game consoles, Blu-ray™/DVD players and/or streaming devices such as Roku™ or Apple TV®. There will also be a number of audio ins and outs, including speaker outputs for stereo and/or multichannel systems and possibly a dedicated phono input for connecting turntables — a must if you’re into vinyl. Don’t make the mistake of assuming that you’ll only need a handful of inputs and outputs; even if your current system is on the modest side, there’s a pretty good chance you may want to expand it in future. It’s always best to plan ahead, so that you don’t quickly outgrow the gear you buy.
As an example, the entry-level Yamaha RX-V385 AV receiver allows the connection of up to five speakers (front left, right and center, along with rear left and right) and a subwoofer for a total of 5.1 channels (the “.1” is the subwoofer). It also provides three analog audio inputs, three digital audio inputs/outputs and four HDMI video inputs, as well as an HDMI output.
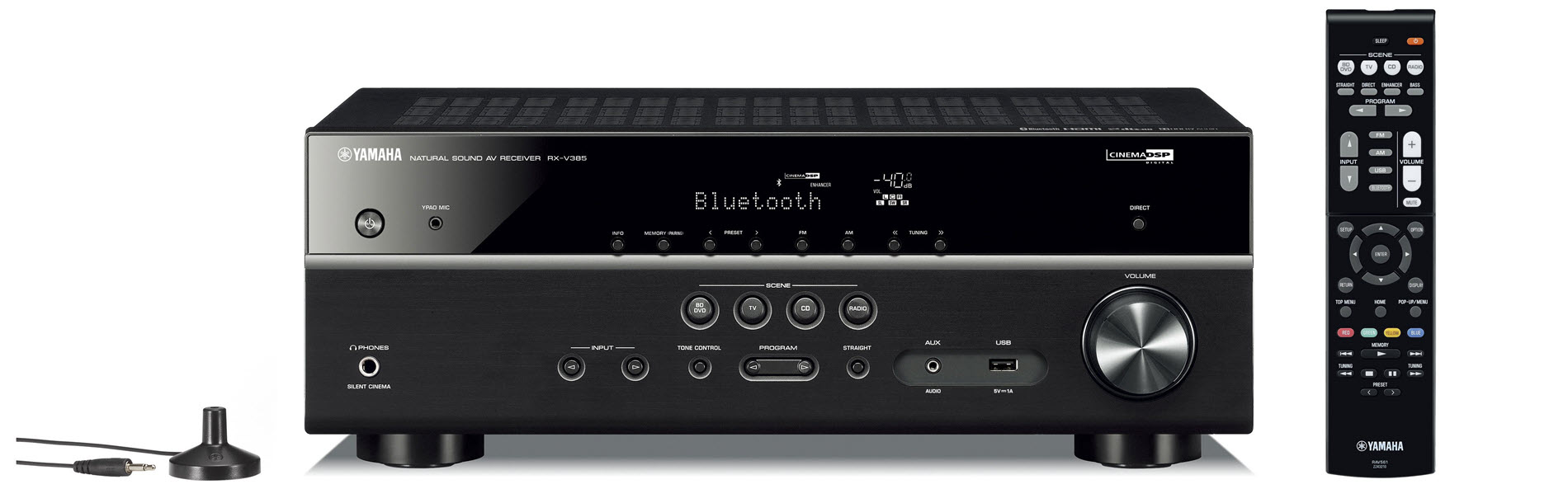

The RX-V4A model offers similar I/O connectivity, but gives you the ability to add a second subwoofer so you can enjoy a 5.2-channel listening experience.
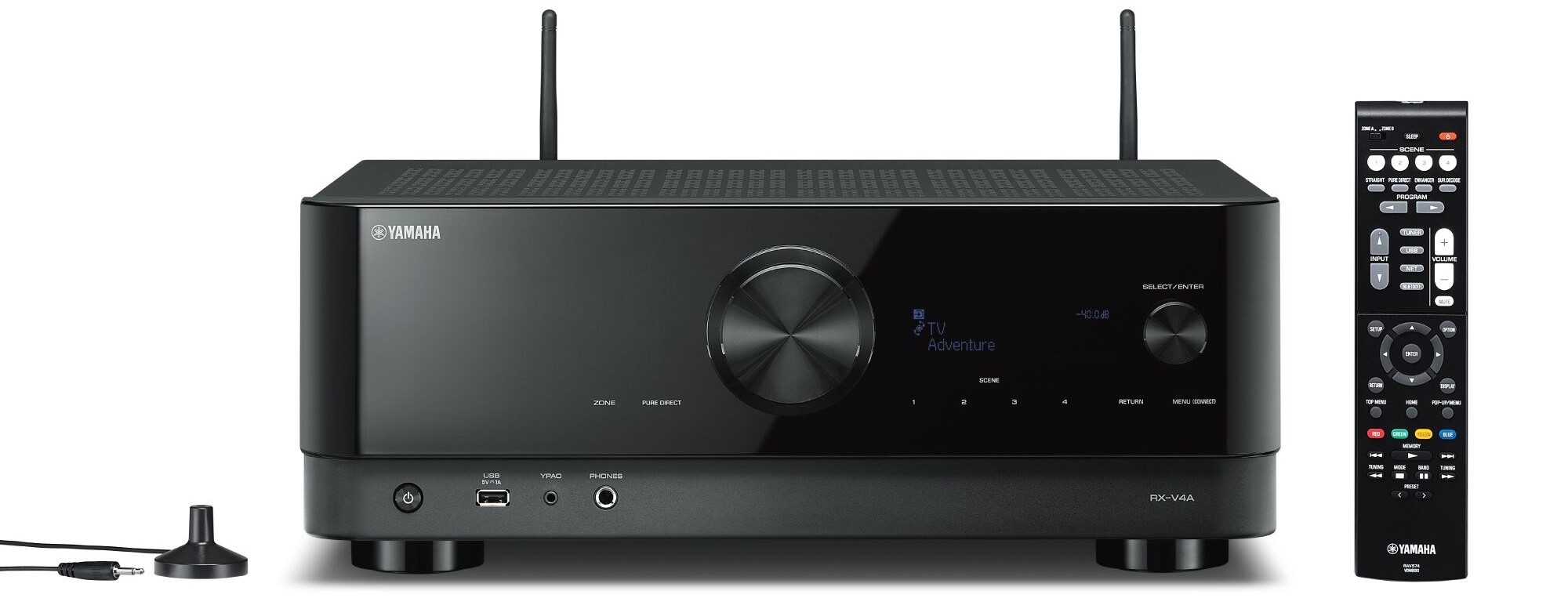

The mid-level RX-V6A expands on that further still by allowing you to connect two additional speakers for 7.2 channel playback, along with providing four analog audio inputs, a dedicated phono input and seven HDMI video inputs.
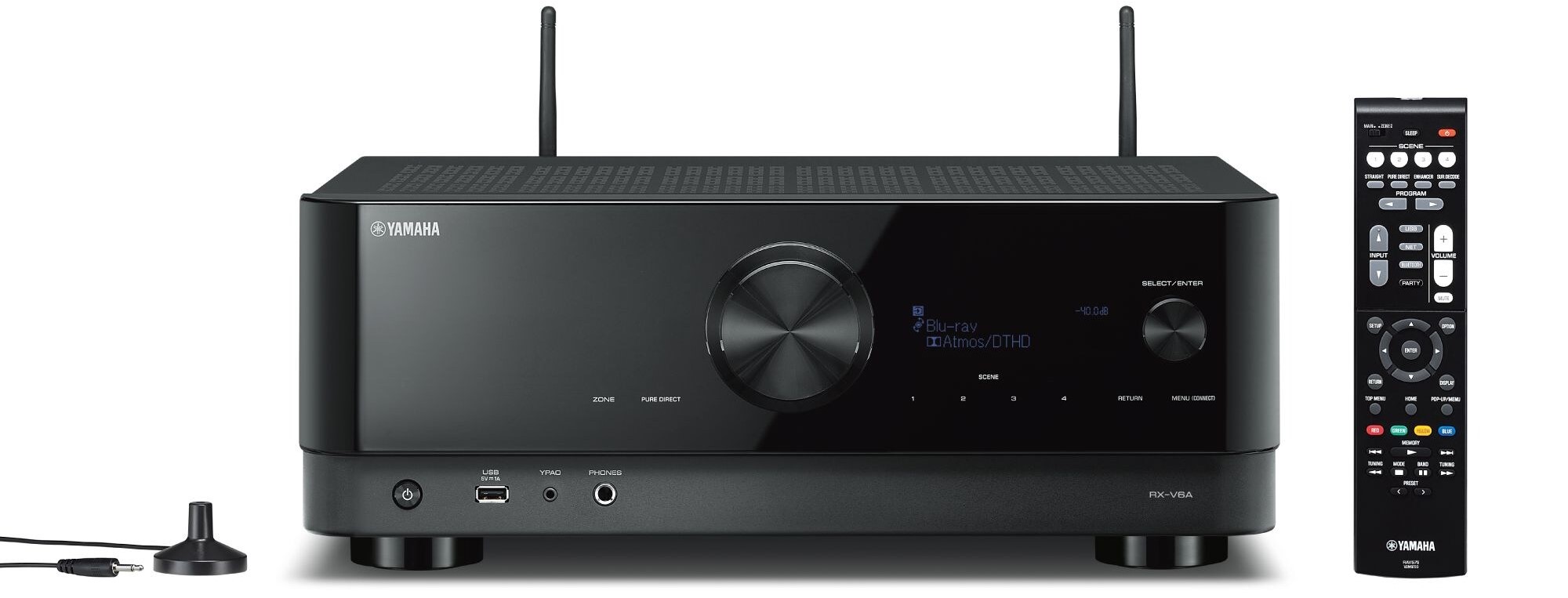

And then there’s the top-of-the-line RX-V8A, which provides full 11.2 channel playback, along with ten analog audio inputs, a dedicated phono input and seven HDMI video inputs.

Power Rating
The more power an AV receiver has (measured in wattage), the louder the playback can be. Having a receiver with an excess of power is generally desirable since it provides extra headroom, meaning that it can get a lot of loudness out of your system without having to be turned up very high, so there’s less chance of distortion. On the other hand, you don’t want the power rating to be so high that you run the risk of damaging your speakers.
The best rule of thumb is to match the power capacity of your AV receiver to that of your speakers as closely as possible. 50-100 watts per channel will provide more than enough volume for most home listening. (Bear in mind that wattage ratings are logarithmic, not linear, meaning that 100 watts is not twice as loud as 50 watts — in fact, it’s only slightly louder.) The aforementioned Yamaha RX-V385 offers 70 watts per channel; the RX-V4A offers 80 watts per channel; the RX-V6A offers 100 watts per channel; and the RX-V8A offers 150 watts per channel, making each of these models eminently suitable for most home theater applications.
Surround Sound Decoding and Processing Capability
Stereo may be fine for casual music listening, but if you want a true cinematic experience when watching your favorite movies and TV shows, you’ll definitely want to opt for a surround sound system. This means that your AV receiver will have to have multiple speaker outputs (as the RX-V385, RX-V4A, RX-V6A and RX-A8A all do, as noted above) and it will also need to be capable of decoding the various surround sound formats commonly used for streaming audio and video.
These formats include Dolby TrueHD®, Dolby DigitalPlus® and DTS-HD Master Audio™ — all supported by the RX-V385, RX-V4A,RX-V6A and RX-V8A; the latter two also provides support for DTS:X™, Dolby Surround® and Dolby Atmos®. (The RX-V6A and RX-V8A even offer Dolby Atmos Height Virtualization technology for the extra envelopment of height channels … but without having to add any additional speakers.)
Audio processing (sometimes called DSP — short for “Digital Signal Processing”) is utilized by most contemporary AV receivers to enhance audio signals in a variety of ways, including being able to isolate dialog so that you can make it louder or softer without altering background music and/or sound effects. Technologies such as Yamaha SILENT CINEMA (offered by the RX-V385, RX-V4A, RX-V6A and RX-A8A) can also simulate various sound spaces when listening with headphones, optimized for a variety of categories in both video and music — for example, Adventure, Drama, Sci-Fi, concert hall, club, or small room. If you only have stereo speakers, you can simulate surround sound with the Virtual Cinema DSP feature offered by many Yamaha receivers, including the three models discussed here.
DSP can also be used to automatically adjust dynamic range — the difference between the loudest and softest sounds. In Yamaha AV receivers such as the RX-V4A, RX-V6A and RX-V8A, this is called Adaptive DRC (Dynamic Range Control). It’s especially important when connecting gaming consoles to an HDMI input on your AV receiver, since it will ensure that, whatever game you’re playing, the volume doesn’t exceed an optimal listening level during the loudest moments.
Wireless Connectivity
It’s important for an AV receiver to be able to connect to the internet via your home network — in fact, it’s a necessity for streaming online content. A network connection also lets you access music libraries and other content you have on your mobile devices or home computers. Many contemporary AV receivers, including the Yamaha models described here, provide Bluetooth® support, allowing you to stream music wirelessly from smartphones, tablets, laptops and other devices into your receiver and then route it to your speakers.
In addition to Bluetooth, the Yamaha RX-V4A, RX-V6A and RX-V8A offer numerous wireless streaming options, including Wi-Fi, AirPlay 2® and Spotify Connect. These allow you to easily listen to your favorite music on services such as Pandora®, Spotify®, Amazon Music, SiriusXM, TIDAL and Deezer. They also provide support for Yamaha MusicCast multi-room technology, which enables you to control all functions remotely from a free app, as well as giving you the ability to connect optional wireless surround sound speakers.
Some MusicCast-enabled AV receivers (such as the RX-V6A and RX-V8A) also provide support for multiple zones, meaning that in addition to your main listening room, you can also listen to the same, or a different, source in another room or zone. If, for example, your family room or home theater room is where your AV receiver lives, you can designate that room as your main zone and outdoor speakers on the patio as Zone 2, allowing you to easily send music from your receiver to the patio simply by pressing a few buttons.
Other Audio Features
Another important audio feature is eARC (short for “enhanced Audio Return Channel”), which you’ll find in all three of the Yamaha AV receivers described here. You may already be familiar with ARC, which allows audio to be sent from your TV to your AV receiver through the same HDMI cable that carries the video signal in the other direction, from your AV receiver to the TV. The “enhanced” part of eARC increases bandwidth, which allows the transmission of full high-res multichannel audio without downmixing the signal to two channels as a means to conserve bandwidth. In addition, eARC allows surround sound signal to be sent uncompressed to your receiver, so you can enjoy theatrical 3D immersive sound from movies offered by Netflix®, Amazon Prime® Video and many other streaming services. And because you don’t need extra wiring to get sound from TV-based apps to play through your receiver, you can use your smart TV as your main streaming video source and enjoy full surround sound through a single HDMI cable.
Some AV receivers, including the three models listed here, also allow you to automatically tune your system based on the acoustics of your room. In the case of Yamaha AV receivers, this technology is called YPAO (short for “Yamaha Parametric room Acoustic Optimizer”).
And audiophiles will appreciate the Pure Direct mode offered by many Yamaha AV receivers, including the RX-V4A, RX-V6A and RX-A8A. When engaged, it feeds sound directly to the onboard amplifier and bypasses any DSP processing that might otherwise color the signal, ensuring the best possible high-fidelity sound from all audio sources — even those coming via USB and HDMI inputs. The end result is a more realistic sound and a deepening of the listening experience, making it more enjoyable than ever.
Video Features
Of course, picture quality is paramount. If you have a recently purchased a big-screen TV or are planning on buying one in the near future, you’ll definitely want to pair it with an AV receiver that has the ability to send incoming video to your TV or projector in up to 4K resolution. Such is the case with all three receivers listed here. The RX-V385 also provides support for several enhanced video modes that offer even better picture quality, including 4K Ultra HD, HDR10, Dolby Vision, Hybrid Log-Gamma and BT.2020; the RX-V4A, RX-V6A and RX-A8A models up the ante with 8K HDMI passthrough and support for HDR10+, which delivers four times as much brightness as standard HDR.
Gaming Support
If you’re an avid gamer, you’ll want to choose an AV receiver that provides features specifically designed to improve the gaming experience, such as ALLM (Auto Low Latency Mode) and VRR (Variable Refresh Rate), both supported by the Yamaha RX-V4A, RX-V6A and RX-A8A.
ALLM, sometimes known as “gaming mode,” tells the receiver to turn off all of its video processing so that the delay (latency) to display gaming video is minimized. VRR gives the AV receiver the ability to automatically vary the frame rate to match the output of the onboard graphics processor (GPU). It enables more fluid and detailed gameplay by reducing or eliminating lag and judder — jittery images caused by upscaling to the 60 frames per second (fps) required by a 60 Hz television and above — plus it reduces or eliminates frame tearing, which occurs when the frame rate exceeds the monitor or television’s refresh rate.
The end result? More realistic visuals to accompany the great audio being delivered by your surround sound system. Game on!
Learn more about the Yamaha RX-V385, RX-V4A, RX-V6A and RX-V8A AV receivers.